Category: Camera repair
-
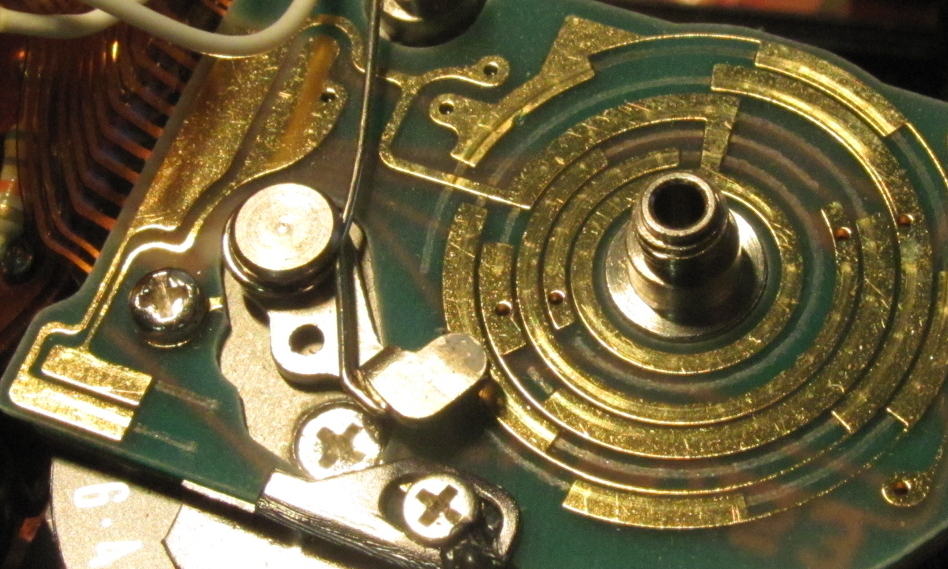

Canon A-1 Mode Switch Repair
My Canon A-1 (which I fixed the wheeze on here but please don’t use that method because it’s a bad hack that could cause more harm than good) was doing something weird. Every so often, when taking a photo indoors in aperture priority mode (Av), I would notice that the camera’s settings would jump to…
-
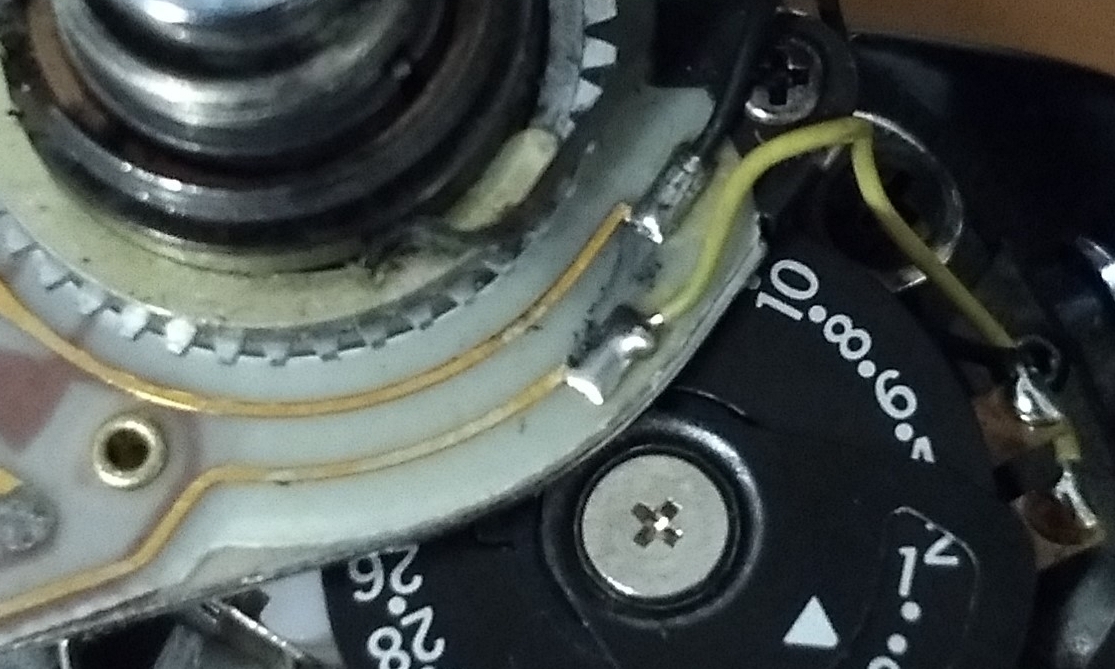
Nikon FG Early Activation Hack
While I was working on the light meter for the Nikon FG, I thought of a ‘fix’ that I’d read about for another issue – making the light meter active as soon as the film door is closed. The FG, by default, will only activate its light meter after the film counter is on 1.…
-

Nikon FG Light Meter Alignment
When I acquired an old family friend’s photographic enlargers a couple of years ago, they threw in a bag of other gear. In the bag was a Nikon F4 (still haven’t got it working – one day!) and a couple of lenses: a Series E 100mm and a Nikkor-H 85mm f/1.8. Too much fine glass…
-

Minolta X-9 Top Plate Removal and Reassembly
I posted these instructions over on Photrio, but thought I’d post them here as well. In my last post, I replaced a dud capacitor on a Minolta X-9 that I was given by a friend. The Minolta X-9, otherwise known as the X-300s I believe, is similar to the X-300 and other X-series cameras, but…
-
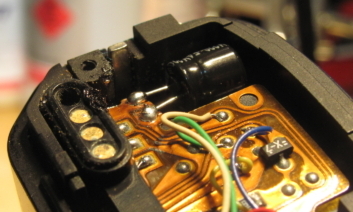
Minolta X-9 Capacitor Replacement
Last year I bought three enlargers from a family friend, who also threw in a bag of other camera stuff. This included a Nikon F4 and a Minolta X-9, neither of which worked properly. The F4 is my dream fix, but it’s a complicated beast. The X-9 (also called/very similar to the X-300S or X-370N)…
-

Minolta XE-5 Film Advance Repair
A couple of months ago, just before the birth of my son, I fixed the film advance on my Minolta XE-5. The lever had not been completing its action properly, and when it got to the end of its rotation there would still be some film winding left to do, so it would just return…
-
Voigtlander Vito CLR – Parts Bin Restoration Part 2
Restoring a camera is a twofold operation. You can restore a camera’s function, get it taking photos reliably, make it work the way it should (or as close as possible to how it should). But you can also restore a camera’s appearance, make it look the way it should. On some level, I’m less concerned…
-
Voigtlander Vito CLR – Parts Bin Restoration Part 1
Judging by the bulk of my recent camera acquisitions, I have a thing for trying to restore and recover the unloved. This started a while ago, I believe, with my Dad’s old Voigtländer Vito CD. It is clearly broken, and its shutter is gummed up to the point it doesn’t open willingly. I have a…
-
Canon A-1 wheeze fix
Edit 2024: DO NOT USE THIS METHOD. The only way to safely lubricate this part is to open the camera. Anything else risks creating an even larger mess. It was bad advice, and I’m only leaving it on here to show that the camera repair learning journey can sometimes take you down the wrong path,…
-
Tokina SD 28-70mm lens focus ring repair
A little while ago, I wrote about fixing the zoom ring on the Tokina SD 28-70mm lens that I got with a parts camera. Fixing the focus ring took a little more effort, and it needed to be done during the day so I could test infinity focus with a distant object, but it followed…
-
Tokina SD 28-70mm lens zoom ring repair
I recently bought a camera as parts, and it came with a Tokina SD 28-70mm 1:3.5-4.5 lens. This lens was in a bit of a state, and I already have a Canon 35-70mm FD mount zoom, but I felt like I had to at least try to repair it on principle, you know? The optics…
-
Ricoh 500G light seal repair
During a trip to Canberra, I dropped in to the Canberra Photographic Market and picked up a Ricoh 500G from a parts bin for $10. The camera was reportedly in “probably fine” condition, but was half way through a light seal repair. I finished cleaning it up (using lens cleaning fluid – not optimal, but…
-
Canon FT QL mirror damper replacement
I thought I’d make my first post about some work done on my favourite camera: my dad’s old Canon FT QL. This fully mechanical SLR was built from 1966-72. It has through-the-lens metering (the only electrical function) and a nifty Quick Load system for film insertion (honestly not sure why it’s not ubiquitous in later…